最近我们遇到了一个生产服务 OOM 的故障,由于问题的根因比较隐蔽,前后定位修复总共耗时近一个月。
起因
一个月前,我们生产服务的一个 pod 重启了,收到告警后,我们检查了 pod 事件,发现是健康检查失败,kubelet 自动重启了 pod。查看 pod 日志,未发现任何报错;检查接口请求量,未发现流量突增;检查 CPU 和内存占用,未超过设置的 limit。此时,我们认为可能是偶发的网络波动导致,决定再观察看看是否会复现。
初步定位
过了几天,同一个服务的另外两个 pod 也重启了,现象完全一样。我们意识到应该是有问题了,于是仔细排查了全部的监控指标,发现在 pod 重启时,堆内存几乎耗尽,服务 full GC 的次数突增,GC 耗时达到数秒,并且老年代对象并未随 full GC 减少。这证实了服务存在内存泄漏,full GC 时 Stop-The-World 导致服务暂停,从而没能响应 kubelet 的健康检查,于是被重启。
发现是内存泄漏之后,就需要进行 heap dump 来分析,不过由于服务 pod 都重启过了,堆内存使用率已恢复正常水平,此时已难以进行定位,于是只能让服务多运行一段时间,等堆内存使用率升高之后再进行排查。
heap dump 分析
又过了十几天,我们再次检查服务的堆内存,发现使用率已接近 80%,并且能明显看到老年代的占比是逐天升高的,于是我们在 pod 内进行 heap dump:
jmap -dump:live,format=b,file=/tmp/heap.hprof 1将 hprof 文件导入到 IDEA 进行分析,发现有 2800 万个 ConcurrentHashMap 的 Node 对象,占用堆内存 1.48 GB:
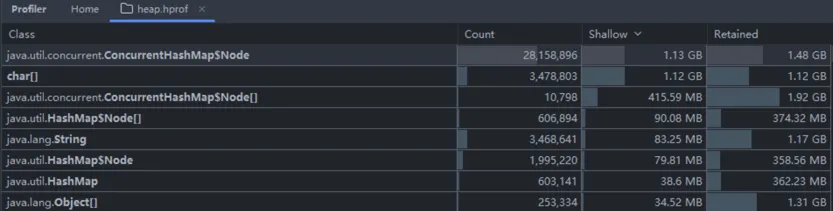 查看大对象,发现主要都是 jasypt 的 EncryptableMapPropertySourceWrapper:
查看大对象,发现主要都是 jasypt 的 EncryptableMapPropertySourceWrapper:
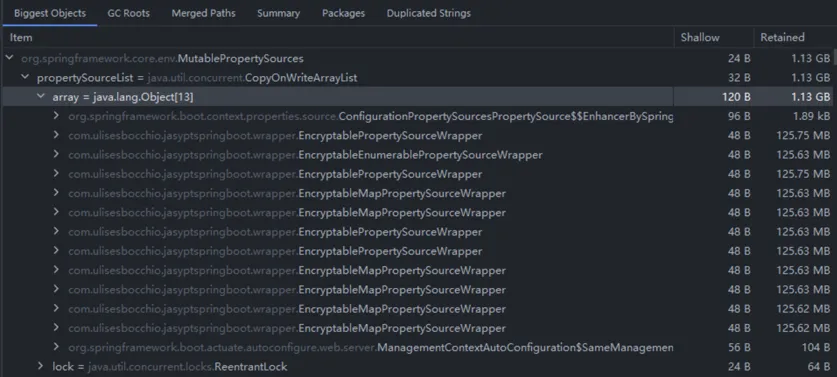 查看 ConcurrentHashMap 的详情,发现存在很多相同 regionMapping 前缀的 key:
查看 ConcurrentHashMap 的详情,发现存在很多相同 regionMapping 前缀的 key:
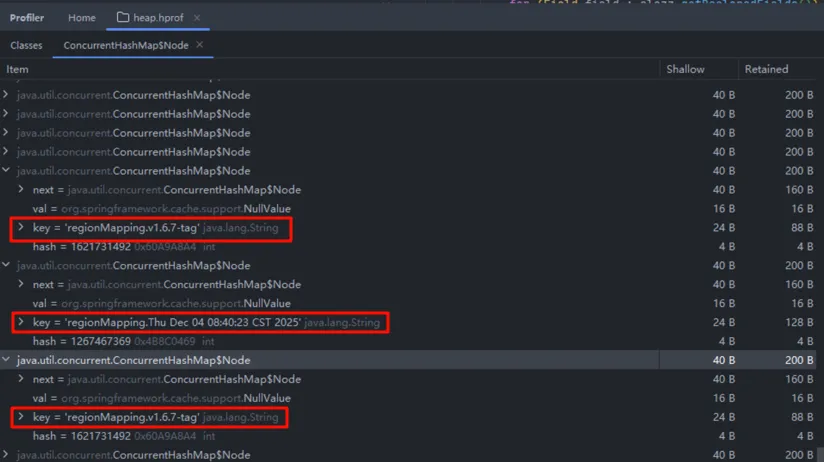 在项目中全局搜索一下,找到了对应代码:
在项目中全局搜索一下,找到了对应代码:
ApplicationContextUtils.getContext().getEnvironment().getProperty("regionMapping." + val);这段代码位于一个 SQL 拦截器中,val 是 SQL 中的字段值,也就是说对于 SQL 的每个字段值这行代码都会去配置文件中查询对应的配置项。问题是,这只是个读操作,怎么会导致数据写入呢?于是我们看了下 jasypt EncryptableMapPropertySourceWrapper 的源码:
package com.ulisesbocchio.jasyptspringboot.wrapper;
import com.ulisesbocchio.jasyptspringboot.caching.CachingDelegateEncryptablePropertySource;
import com.ulisesbocchio.jasyptspringboot.EncryptablePropertyFilter;
import com.ulisesbocchio.jasyptspringboot.EncryptablePropertyResolver;
import com.ulisesbocchio.jasyptspringboot.EncryptablePropertySource;
import org.springframework.core.env.MapPropertySource;
import org.springframework.core.env.PropertySource;
import java.util.Map;
/**
* @author Ulises Bocchio
*/
public class EncryptableMapPropertySourceWrapper extends MapPropertySource implements EncryptablePropertySource<Map<String, Object>> {
private final EncryptablePropertySource<Map<String, Object>> encryptableDelegate;
public EncryptableMapPropertySourceWrapper(MapPropertySource delegate, EncryptablePropertyResolver resolver, EncryptablePropertyFilter filter) {
super(delegate.getName(), delegate.getSource());
encryptableDelegate = new CachingDelegateEncryptablePropertySource<>(delegate, resolver, filter);
}
@Override
public void refresh() {
encryptableDelegate.refresh();
}
@Override
public Object getProperty(String name) {
return encryptableDelegate.getProperty(name);
}
@Override
public PropertySource<Map<String, Object>> getDelegate() {
return encryptableDelegate.getDelegate();
}
}其中 getProperty 方法使用的 encryptableDelegate 是 CachingDelegateEncryptablePropertySource 类型,看到这个名字里的 Caching 就猜到大概了。再看 CachingDelegateEncryptablePropertySource 的源码:
package com.ulisesbocchio.jasyptspringboot.caching;
import com.ulisesbocchio.jasyptspringboot.EncryptablePropertyFilter;
import com.ulisesbocchio.jasyptspringboot.EncryptablePropertyResolver;
import com.ulisesbocchio.jasyptspringboot.EncryptablePropertySource;
import org.springframework.cache.concurrent.ConcurrentMapCache;
import org.springframework.core.env.PropertySource;
import org.springframework.util.Assert;
public class CachingDelegateEncryptablePropertySource<T> extends PropertySource<T> implements EncryptablePropertySource<T> {
private final PropertySource<T> delegate;
private final EncryptablePropertyResolver resolver;
private final EncryptablePropertyFilter filter;
private final ConcurrentMapCache cache;
public CachingDelegateEncryptablePropertySource(PropertySource<T> delegate, EncryptablePropertyResolver resolver, EncryptablePropertyFilter filter) {
super(delegate.getName(), delegate.getSource());
Assert.notNull(delegate, "PropertySource delegate cannot be null");
Assert.notNull(resolver, "EncryptablePropertyResolver cannot be null");
Assert.notNull(filter, "EncryptablePropertyFilter cannot be null");
this.delegate = delegate;
this.resolver = resolver;
this.filter = filter;
this.cache = new ConcurrentMapCache("encryptablePropertiesCache");
}
@Override
public PropertySource<T> getDelegate() {
return delegate;
}
@Override
public Object getProperty(String name) {
return cache.get(name, () -> getProperty(resolver, filter, delegate, name));
}
@Override
public void refresh() {
cache.clear();
}
}果然,这里使用了 ConcurrentMapCache 来缓存每次 getProperty 的结果。
jasypt 是个常用的 spring 配置加解密库,它支持 ENC() 格式加密配置项,防止敏感信息明文暴露。由于每次读取配置需要进行解密,jasypt 便缓存了解密结果来防止重复解密带来的不必要的 CPU 消耗。没想到的是,这个优化手段由于我们的动态读取,最终导致了内存泄漏。
总结
jasypt 会缓存 spring 的配置读取结果,读取配置时要避免动态读取,防止缓存无限增长导致内存泄漏。读取配置时,可以先全量加载到内存中,随后再进行检索,即可避免类似问题。